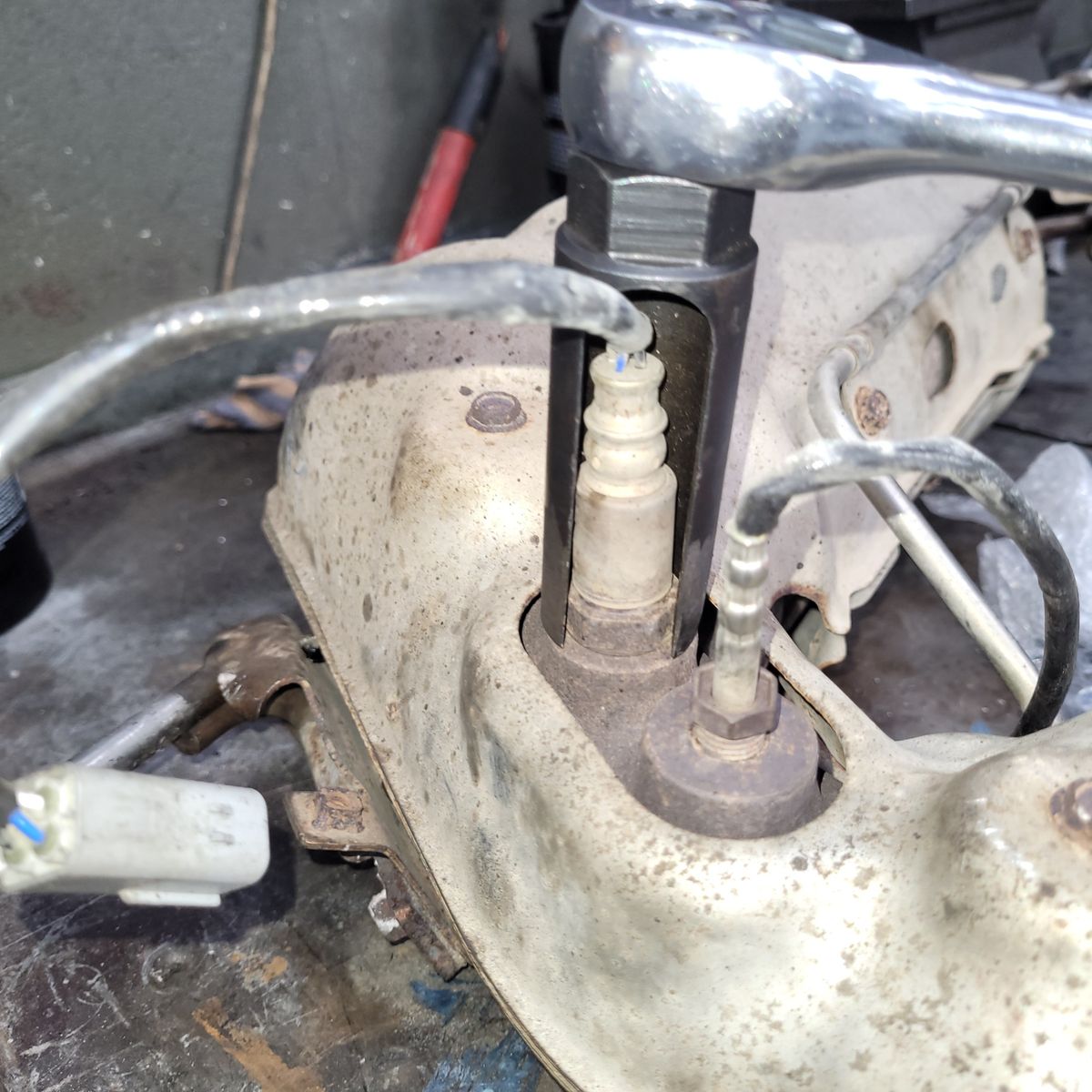
About Oxygen Sensors (O2 Sensors):
Most everyday combustion engines work by exploding a combination of air and fuel. Oxygen sensors are used to create the optimal fuel efficiency in your car. Oxygen sensors constantly detect the oxygen content of a car’s exhaust emissions. The oxygen sensor will then tell the car’s computer (ECU) whether the air to fuel content ratio in the exhaust is rich (High in fuel, low in oxygen) or lean (High in oxygen, low in fuel). Using this information, the car engine computer will then adjust the fuel injection amounts to create the best ratio of air and fuel, and the best efficiency. Oxygen sensors are usually screwed into the exhaust near the exhaust manifold.
Learn more about oxygen sensors

How serious is a damaged oxygen sensor:
A faulty oxygen sensor will bring up the Check Engine Light (CEL) on your dash. This is because the Oxygen Sensor is generally the last major sensor in the engine and therefore gives the engine computer vital information about how well the engine is running. The downside of a failed Oxygen Sensor would be the increased running cost due to significantly lower fuel efficiency, poor engine performance (lack of power), possibly rough idle, and more.
Diagnostics:
The fault codes P0030 – P0175 are OBDII diagnostic fault codes for an oxygen sensor (O2 Sensors). These fault codes are generated when an an oxygen sensor and engine car computer try everything they can to get a good Air – Fuel ratio but are unable to. In this case the check engine light will be on. As some cars have more than one O2 Sensor, there are a large number of fault codes. The most common O2 sensor fault codes are:
- – O2 Sensor Circuit Malfunction – Codes for each sensor include: P0130, P0136, P0137, P0142, P0150, P0152, P0156, P0162. These can be caused by a disconnected sensor, short, broken sensor element or circuit component or a thermal shock.
- – O2 Sensor No Activity Detected – Codes for each sensor include: P0134, P0140, P0146, P0154, P0160, P0166. These can be caused by a short causing the sensor to not work, or deposits poising the air measurement electrode.
- – O2 Sensor High Voltage – P0138, P0144, P0152, P0158, P0164. These can be caused by a short, or the sensor being immersed in water or carbon.
- – O2 Sensor Low Voltage – P0131, P0151, P0157, P0163. These can be caused by a short between ground and the signal wire, deposit poisoning or failed heater circuits.
- – O2 Sensor Circuit Slow Resistance – P0133. Caused by carbon deposits, silicon or ethylene glycol poisoning.
- – O2 Sensor Circuit Slow Response – P0139, P0153, P0159, P0165. These can be cause by carbon deposits, or silicon poisoning, failed sensor heaters or a blown heater circuit fuse
- – O2 Sensor Heater Circuit Malfunction – P0135, P0141, P0147, P0155, P0161. P0167, These can be caused by a shorted or open heater circuit. Sensor installed with incorrect current values, blown heater circuit fuse.
- – Fuel Trim Malfunction – P0170, P0173, This can be caused by vacuum air or fuel leaks, or just a bad sensor.
- – System to Lean – P0171, P0174, This can be caused by Air or vacuum leaks or damaged fuel pumps, injectors or O2 Sensors.
- – System to Rich – P0172, P0175, This can be caused by vacuum air or fuel leaks, or just a bad sensor.
These and other fault codes also apply to Heated Oxygen Sensors.
For more information and fault codes for each sensor, please visit: O2 Sensor – OBDII Codes
Possible causes of a damaged oxygen sensor:
– Water Damage: If any rust or corrosion is visible or present around any part of the oxygen sensor, it is likely the sensor is damage due to water.
– Oxygen Sensor Deposits: If the sensor has any kind of deposit such as carbon, oil, lead or white, grey and shiny deposits are visible on the oxygen sensor, the sensor is likely to be damaged. These deposits can eat away at the sensor or cover the sensor meaning it may give bad readings.
– Damaged oxygen sensor circuits: It is possible that oxygen sensor circuits or oxygen sensor heater circuits malfunction, meaning damage has occurred to the sensor, or the sensor may not work.
Symptoms of a damages oxygen sensor:
– Check Engine light – This will be switched on if a good Air to Fuel ratio cannot be achieved and may indicate a faulty oxygen sensor
– Less fuel mileage – If you notice yourself turning up at the petrol station more often, it could be because of a damaged oxygen sensor. If a oxygen sensor is damaged and providing incorrect data it will result in your car being far less fuel efficient.
– Visible emissions – If you’re car is producing constant visible emissions it is possibly due to a faulty oxygen sensor. This could mean that the oxygen sensor is not providing accurate data so your air to fuel ratio will be significantly incorrect. This means your car will produce excess emissions which may be visible.
Oxygen sensor replacements in Hamilton:
Without seeing and testing your car, it is very hard for our mechanics to correctly diagnose a problem with your oxygen sensor.
At Grimmer Motors, we provide a variety of diagnostic services. When you bring your car into Grimmer motors we will try always try to be absolutely certain of the problem with you’re oxygen sensor before we start replacing parts. This means we will use our Live Data scan tools, Oscilloscopes, Ohmmeters and visual inspections etc, to accurately diagnose and repair you’re car.
Our experienced mechanics can easily diagnose and replace a faulty oxygen sensor.
For all diagnostic checks or oxygen sensor replacements in Hamilton, contact Grimmer Motors today!