Quick chat about car fuses
Alright, here’s the lowdown. Car fuses are those little bits that sit quietly in your car, but when something electrical goes wrong, they’re the first to stick their hand up and cop the blame. Blown a fuse? It’s usually doing its job – protecting the wiring in your Mazda Demio, Honda Jazz, or your old Mitsi Outlander from overloading or shorting out, especially with all the weird weather we get around Hamilton.
Honestly, with all the stop-start driving on Victoria Street, over those speed bumps in Claudelands, or cruising the pothole-riddled streets out Morrinsville way, the electrics in your car have a rough life. If a fuse blows, whatever it’s protecting, like your speakers or wipers, just stops dead. No power’s getting through. Swap the fuse, and you’re away laughing.
Want to go deeper on the science bit? There’s a good yarn here about how fuses work: Learn more about how fuses work >
How can you tell if a car fuse is blown?
Here’s the stuff we see around the workshop all the time:
- Something stops working: Classic case – a Toyota Corolla or Kia Carnival rocks up and the A/C’s stone cold dead or the radio’s silent. Blown fuse is usually top of our suspect list.
- Bulb’s out (but not blown): We get heaps of people in from Te Awamutu or Cambridge complaining about tail lights or indicators not working, especially in winter when you actually need them! Sometimes it’s not the bulb that’s shot, it’s a simple fuse.
- Car won’t start: Seen this heaps with older Nissans and even a couple of Renaults. Sometimes there’s a short and the fuse for the fuel pump or ignition’s blown, so you’re stuck outside The Base with a car that won’t even turn over.
- Dashboard lights up like a Christmas tree: If that ABS or check engine light pops on after a jolt on Peachgrove Road, could be a fuse related to one of those big systems. Annoying, but usually not a huge fix.
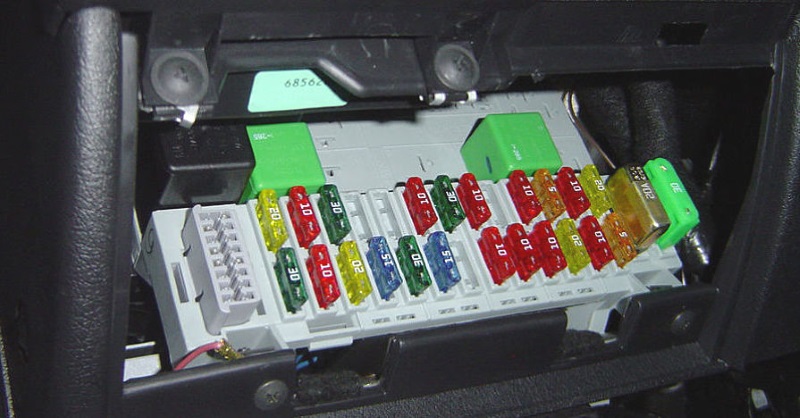
So where do you find car fuses?
Location’s different for everyone, depending where the factory decided to stick ‘em! Always check your manual if you’ve still got it. Around Hamilton, we see most fuse boxes:
- Under the steering wheel, sometimes behind a pop-off panel
- In or under the glovebox (Subarus especially love hiding them here)
- In the engine bay, usually in a big black box with a clip lid
Most modern cars like Suzuki Swifts, VW Golfs, or even those Lexus hybrids have two fuse boxes – one inside and one under the bonnet. The inside ones control your radio, lights and wipers (those things you crank flat out in a Hamilton fog), while the engine bay fuses handle bigger jobs – stuff like cooling fans, ABS or the engine computer.
How to check and change fuses without mucking it up
You’ll see all sorts – skinny blade fuses in Mazdas, bigger blocky ones in Euros like Peugeots or Citroens. Most have a little plastic window so you can eye up the wire inside. If it’s broken or looks a bit crispy, she’s blown.
Before you swap it, make sure you grab another one with the same amp rating (they’re colour-coded too – red’s usually 10 amp, for instance). Don’t go whacking a bigger fuse in there thinking it’ll last longer… That can cook your wiring and give you a way bigger headache down the line.
If you’re not sure, or you can’t even find the right fuse let alone pull it out (happens heaps, especially in those tight Euro cars), don’t stress. That’s what we’re here for.
Need a hand with car fuses in Hamilton?
Honestly, it’s not always an easy job, especially if you’re in a hurry or you don’t want to muck around guessing. Whether your Nissan Leaf’s radio is silent, your Audi A3’s wipers have died mid-storm on Pukete Road, or you just can’t find the fuse at all – swing by. One of our techs will hook up quick fuse testing and replacements, get your electrics sorted, and have you back on the road in no time.
We’ve got fuses in stock and we’re happy to explain what’s going on, whether you’ve driven in from Raglan, Matangi, or just around the corner in Hamilton East. If you need a new car fuse or electrical issue sorted, give Grimmer Motors a bell or just book online below.